Introduction
In the world of professional drone operations, everything revolves around precision, safety, and efficiency. A mission flight — an automated flight — enables a drone to follow a pre-programmed route with pinpoint accuracy. This technology opens the door to precise inspections, consistent imaging, and structured data collection. In this article, we explain why mission flights are so valuable, how to set them up correctly, and how Droneview.be uses them to deliver maximum value.
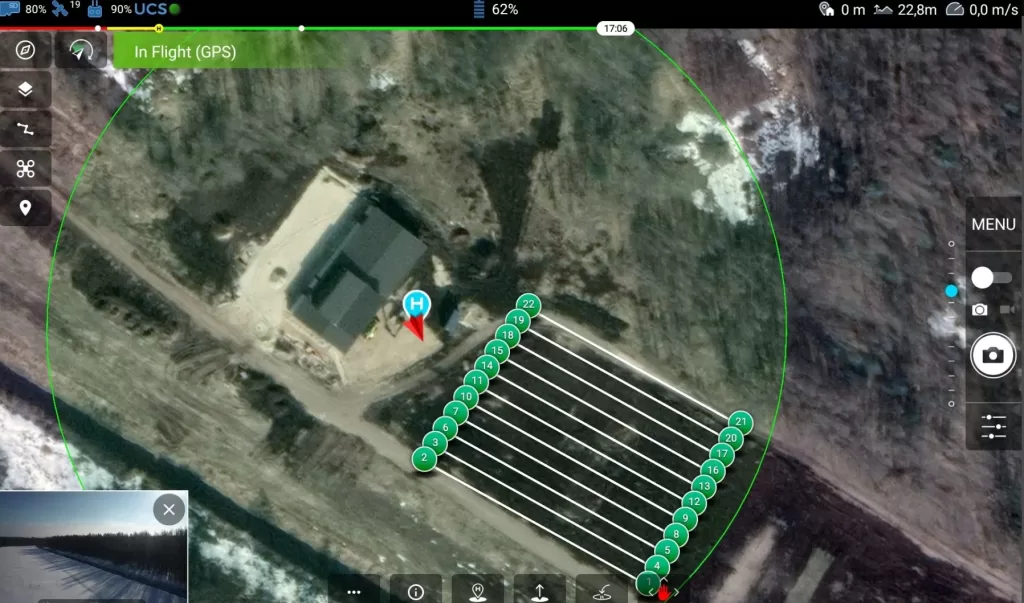
Why Use Mission Flights?
Efficiency
Mission flights save time on-site. You plan the flight in advance, allowing for smooth execution without improvisation.
Accuracy
Flying the exact same route every time means the data or images are perfectly comparable — ideal for construction monitoring or detecting changes over time.
Safety
Less manual input during flight reduces the risk of human error. The drone flies steadily and precisely along predefined waypoints.
Documentation
Most flight apps automatically log flight data, including camera angles, positions, and settings. Perfect for reports or future reference.
Applications
-
Solar park inspections: With automated routes, we can capture each panel systematically and accurately — optionally combined with thermal imaging. See our solar inspection page.
-
Mapping large sites or buildings: Mission flights are ideal for collecting data for processing in WebODM, such as 2D orthophotos or 3D models. See our page on WebODM applications.
-
Construction site monitoring: Repeated flights at fixed intervals allow for precise documentation over time.
Preparation
Compatible Drones
Not every drone supports mission flights. At Droneview.be, we use the DJI M210 and Inspire 2, both of which are compatible with automated flight software.
Software
For most operations, we use the DJI Pilot app — DJI’s professional application for waypoint missions, mapping, and live monitoring. For specific mapping needs, we sometimes use DJI GS Pro or DroneDeploy.

Regulations
Even automated flights must comply with Belgian drone regulations. This includes altitude limits, no-fly zones, and mandatory notifications for specific flights.
Step by Step: Setting Up a Mission Flight with DJI Pilot
1. Define Your Objective
What is the goal? Mapping, inspection, visualization? This determines the approach, settings, and type of mission.
2. Create the Mission
Open DJI Pilot > Go to Mission Flight > Choose either “Waypoint Flight” or “Mapping,” depending on your purpose.
3. Select the Area on the Map
Use the map view to select the area you want to fly over. You can place waypoints manually or auto-generate a grid for mapping.
4. Configure Waypoints or Grid
For each waypoint or grid segment, define:
-
Altitude
-
Flight speed
-
Camera angle (gimbal pitch)
-
Actions at each point (take photo, hover, etc.)
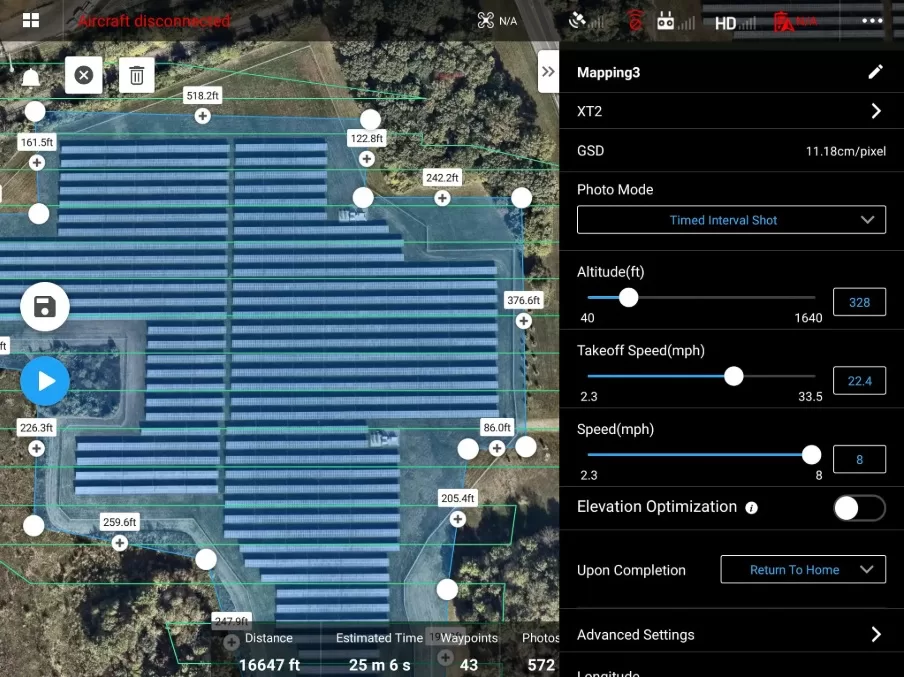
5. Configure Camera Settings
For mapping, set the front and side overlap (e.g., 70% front / 60% side). Choose the correct resolution, ISO, and shutter speed. For thermal imaging, configure the temperature scale or palette.
6. Execute the Pre-Flight Checklist
Check GNSS signal, battery levels, RTH altitude, and IMU status. DJI Pilot automatically provides a checklist before takeoff.
7. Start the Flight and Monitor Live
Launch the mission and monitor it in real-time via the screen. At Droneview.be, we display the live feed on an external 32″ monitor for our clients.
8. Save and Analyze Data
After the flight, all footage and flight data are saved automatically. For mapping, the data is processed in software like WebODM. For inspections, we use targeted imagery for reporting.
Tips from the Field – Droneview.be
-
We often combine mission flights with thermal cameras or zoom lenses for hard-to-reach inspection points.
-
For large-scale projects, we use terrain models beforehand to ensure safety.
-
For recurring flights (e.g., monthly progress reports), we ensure full reproducibility of flight routes and settings.
-
Clients can follow along in real-time via our mobile monitor — providing instant feedback.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
-
Waypoints set too close to obstacles like trees or cranes.
-
Incorrect camera angle or insufficient overlap for mapping.
-
Overlooking failsafe settings for signal loss.
-
Skipping a thorough pre-flight check.
Conclusion
Mission flights are a powerful tool for professional drone pilots. They make your work faster, safer, and more consistent. At Droneview.be, we use this technique daily to deliver reliable data and imagery to our clients. Want to discover how a mission flight can enhance your project? Contact us for a free demo or quote.
